DAMAS
Data Analytics
and
Mobile Autonomous Systems
Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence.
Machine learning explores the construction and study of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms operate by building a model from example inputs in order to make data-driven predictions or decisions, rather than following strictly static program instructions.
Machine learning is closely related to and often overlaps with computational statistics; a discipline that also specializes in prediction-making. It has strong ties to mathematical optimization, which deliver methods, theory and application domains to the field.
Machine learning is employed in a range of computing tasks where designing and programming explicit algorithms is infeasible. Example applications include spam filtering, optical character recognition (OCR), search engines and computer vision.
Mobile Autonomous Systems and Robotics
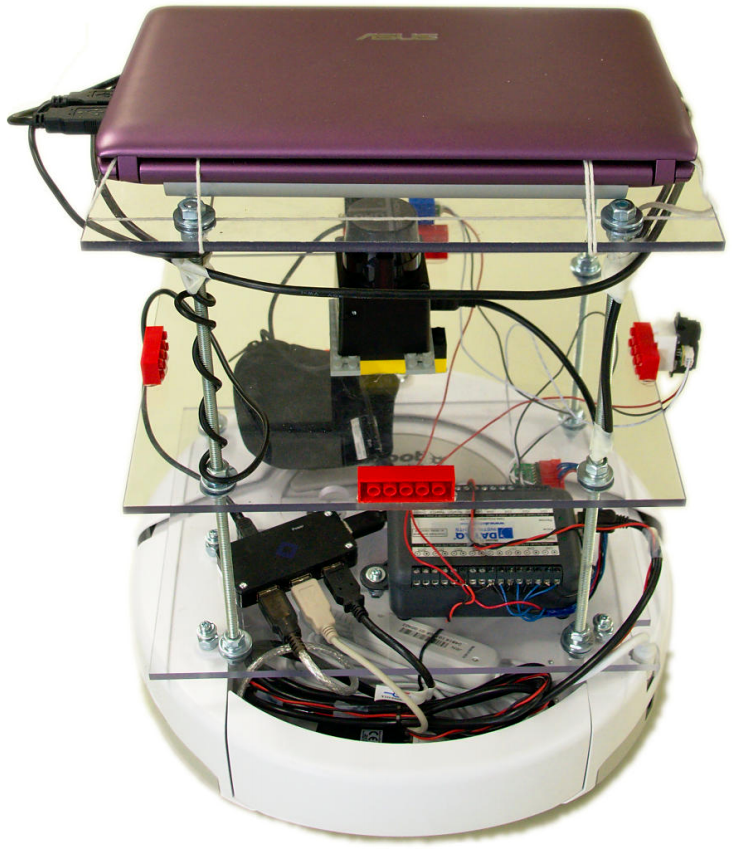

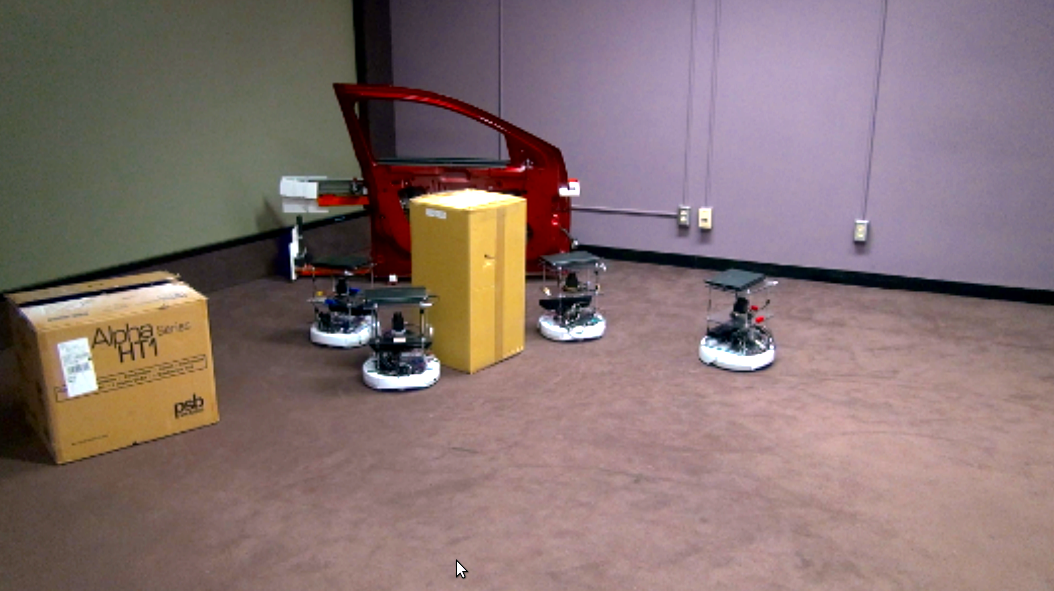
An autonomous robot is a robot that performs behaviours or tasks with a high degree of autonomy, which is particularly desirable in fields such as space exploration, household maintenance (such as cleaning), waste water treatment and delivering goods and services.
Some modern factory robots are "autonomous" within the strict confines of their direct environment. It may not be that every degree of freedom exists in their surrounding environment, but the factory robot's workplace is challenging and can often contain chaotic, unpredicted variables. The exact orientation and position of the next object of work and (in the more advanced factories) even the type of object and the required task must be determined. This can vary unpredictably (at least from the robot's point of view).
One important area of robotics research is to enable the robot to cope with its environment whether this be on land, underwater, in the air, underground, or in space.
A fully autonomous robot can:
- Gain information about the environment.
- Work for an extended period without human intervention.
- Move either all or part of itself throughout its operating environment without human assistance.
- Avoid situations that are harmful to people, property, or itself unless those are part of its design specifications.
An autonomous robot may also learn or gain new knowledge like adjusting for new methods of accomplishing its tasks or adapting to changing surroundings.